Randomness
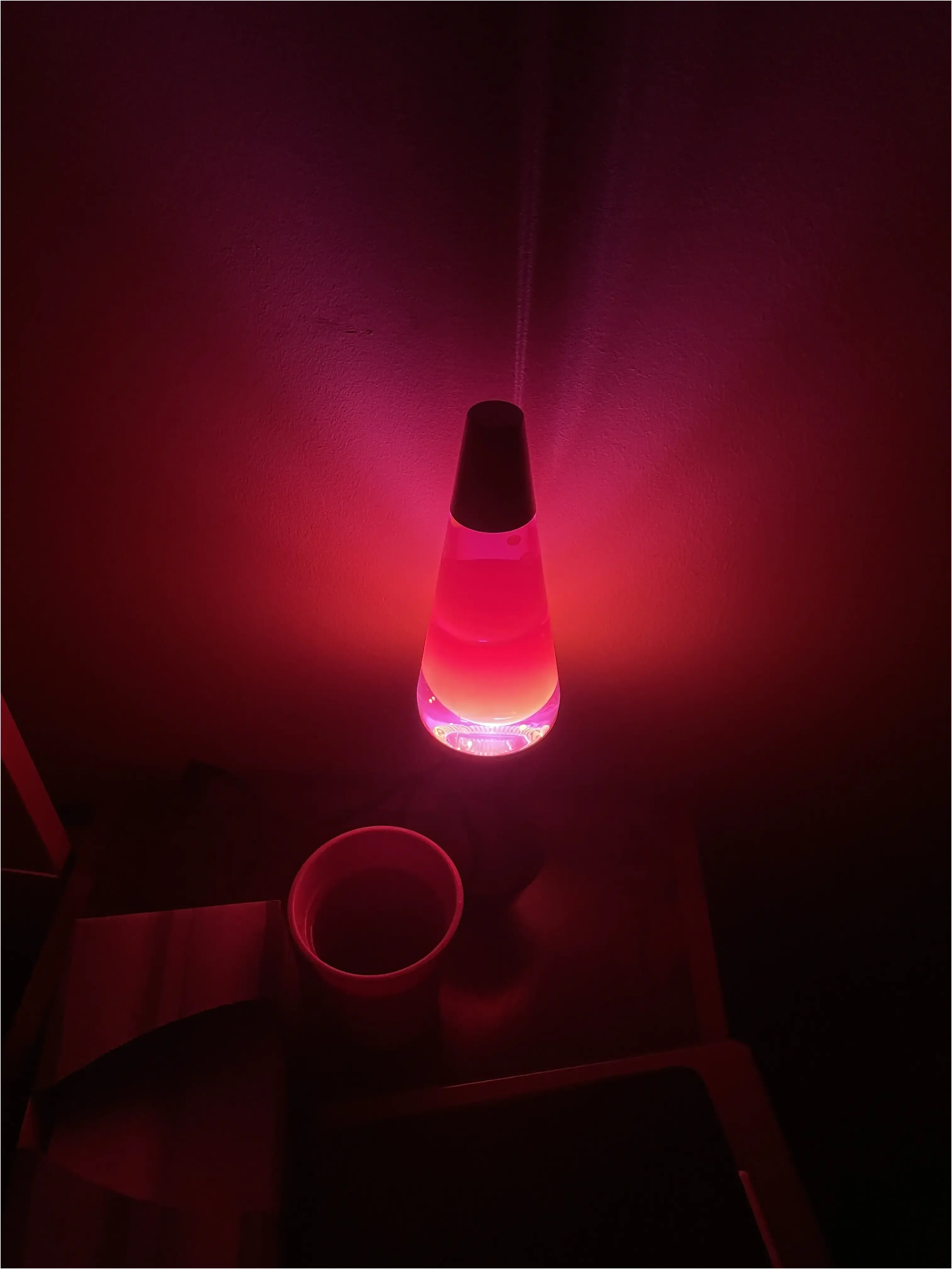
Having real randomness on a deterministic machine is a pretty interesting topic, while one can easily achieve pseudo-randomness by creating a complex algorithm with unpredictable outputs(such as a chaotic system). However, for a microcontroller with the same code whenever it boots up, the above solution will give you the same number every time. So it would be nice to introduce some external chaotic sources, the most commonly used one might be heat noises, which require some kind of temperature sensor. I also heard Lava Lamps are being used as a chaotic source in some real applications - Cloudflare uses 100 such lamps for their random generator - how bizarre!